Making your own Dreamcast MIDI Interface Cable
Saturday, 1st May 2021
I love an unusual accessory for a video game console or computer, and one such accessory is the Dreamcast MIDI Interface Cable, HKT-9200, which allows you to connect MIDI devices to the Dreamcast console's serial port. Only released in Japan and with only one piece of software released for it — the O・to・i・re (お・と・い・れ) sequencer – these are a somewhat hard to find accessory nowadays and prices for second-hand units are far beyond what I could hope to afford (at the time of writing there are two on eBay, both for over £300).
Fortunately, the user darcagn on the Obscure Gamers forum took some photos of the insides of the interface box and from that I could make a pretty good guess as to how the cable works.
MIDI uses a serial protocol running at 31.25Kbps (a speed that can be easily derived by dividing a 1MHz clock by 32). Rather than signal "0" or "1" bits with different voltage levels (as with a PC's RS-232 serial ports, for example, which commonly uses +12V for a "0" and -12V for a "1") it uses a current loop, with 5mA current on for a "0" and current switched off for a "1". To avoid ground loops, which are a big concern when working with audio as they can introduce intereference (e.g. a mains hum) on recordings, the two connected devices are electrically isolated with an optoisolator in the receiver.
At the very least I therefore expected to see some sort of optoisolator circuit on the adaptor's MIDI IN port and some sort of output buffer circuit on the adaptor's MIDI OUT port to convert between MIDI's current loop signalling and the Dreamcast's 3.3V logic on its serial I/O pins, and that is indeed what you can see from darcagn's photos. My worry was that there might be some additional Dreamcast-specific hardware inside the box, but fortunately there isn't – it's all off-the-shelf parts. My main concern was how everything was connected, as this can't be completely seen from the photos: would sending MIDI IN data to the console's serial port RX and relaying data from the console's serial port TX to MIDI OUT be enough? Some experimentation would be necessary!
Building a serial port connector
As mentioned above, the MIDI interface cable's box doesn't contain anything Dreamcast-specific, however this box is connected to the Dreamcast's serial port using a proprietary connector. To try anything out I'd need to find a way to connect a circuit to this port:
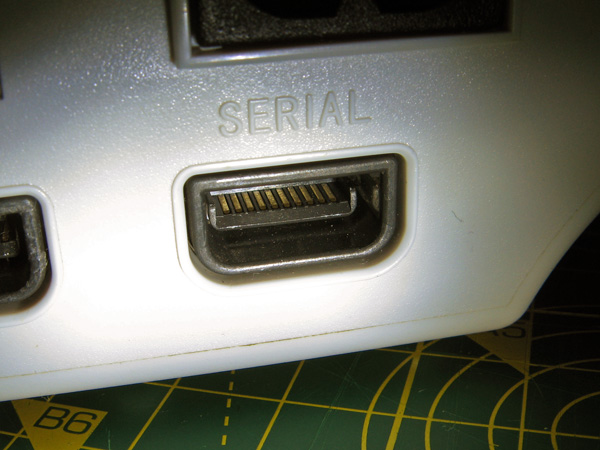

Fortunately, the port's contact pitch is the same as a PCI Express slot, and I was able to find a PCI Express slot for £5 which could be used to make multiple connectors! It will need to be cut down to size (and in half, as the Dreamcast's serial port only has contacts on one side rather than both sides of a PCI Express card) but with a bit of work will do the job.
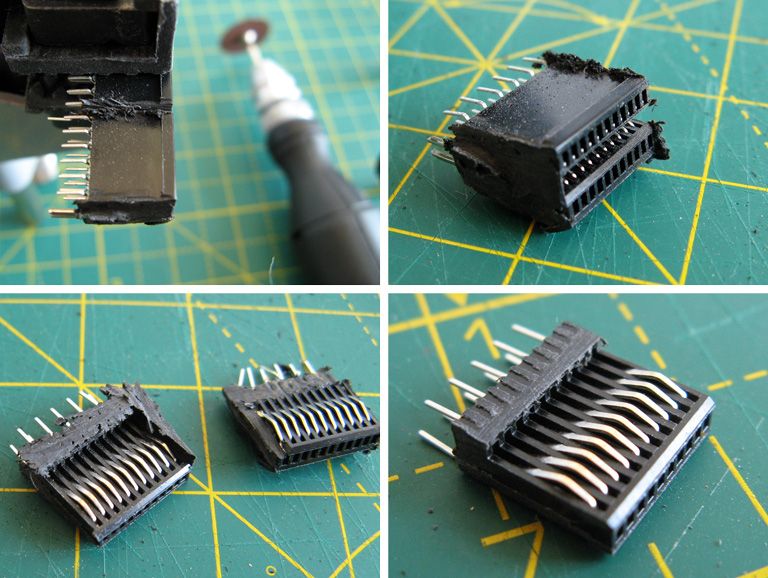

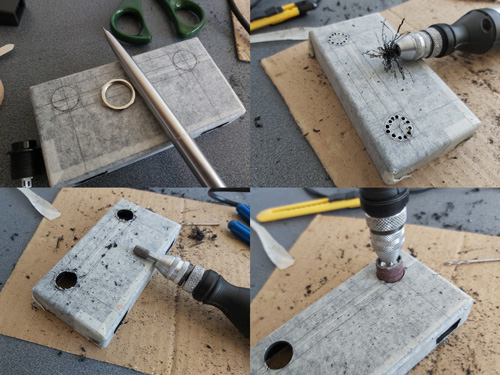
The above photos show the process of cutting the PCI Express slot down to size. The Dreamcast serial port has 10 connectors in it, so a block is cut that is 12 connectors long using a cutting disc – as this is quite a rough process an extra sacrificial connector is left on each end as it doesn't matter if this gets mangled by the cutter. The block is then cut in half, leaving more of the support structure from the bottom of the slot on the side of the slot we're going to be using. The outer two connectors are then removed if they haven't already been damaged, leaving the central 10 connectors, and the outer plastic is brought to the final width and tidied up with some hand files. The fit of the connector should be tested against the Dreamcast's serial port:

There shouldn't be too much side-to-side movement but the connector will be very loose without something to hold it down against the contacts. In my case I found some 2mm thick ABS plastic sheet was the perfect material to make the backing piece for the connector, though you may find your choice of material depends on the thickness of your PCI Express slot. It will need to be 13.5mm wide (about ½") and a decent enough length to fit inside the enclosure you're going to use for the plug – in my case 4cms was about right. The plastic can be cut by scoring it with a knife and then snapping it over the edge of a table.
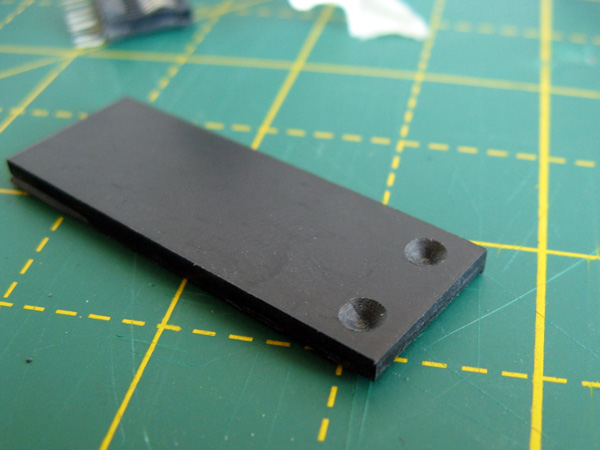

You should also drill some shallow holes in the plastic, with the centres of the holes being 3mm from the end and 3mm from the sides. The serial port has a couple of bumps stamped into the metal surround of the serial port and these matching holes in the plastic piece allow it to snap into place. A stripboard track-cutting drill is perfect for this task!
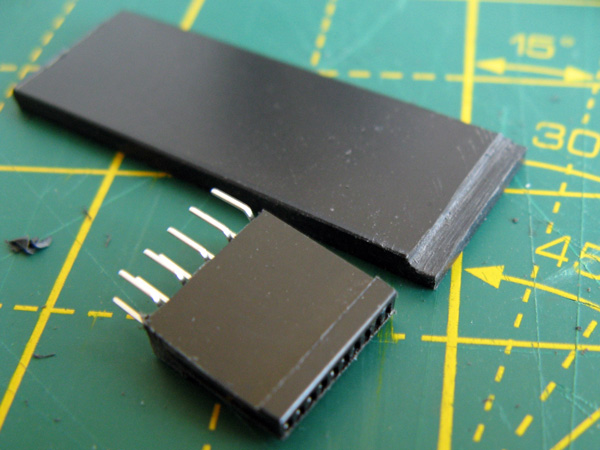
In my case the PCI Express slot also has a slight lip that prevents it from sitting flush against the backing support. I could have filed this flat but the connector is quite fragile so I didn't want to risk damaging it so I ended up filing a corresponding channel into the bottom of the backing support piece.
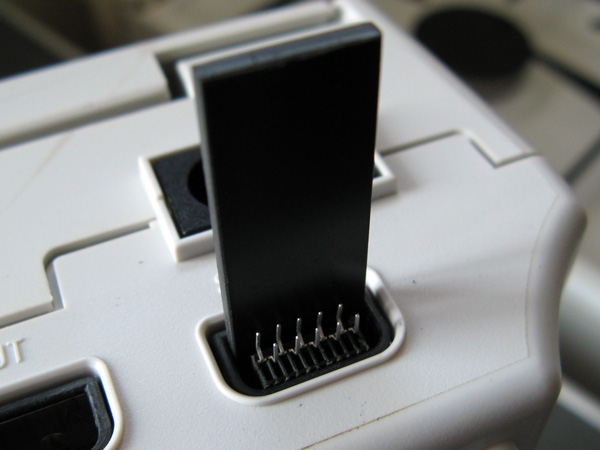

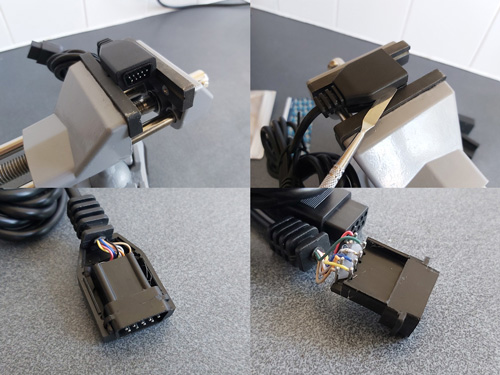
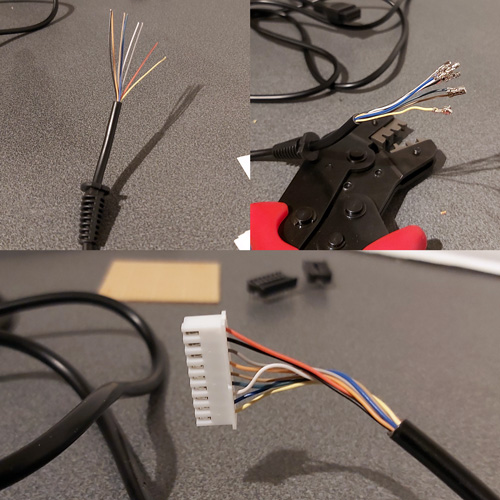
At this point make sure that everything fits. If it does you can start wiring up! The photos below show the process – heat-shrink tubing and strain reliefs are very useful, so don't forget to install them before soldering!
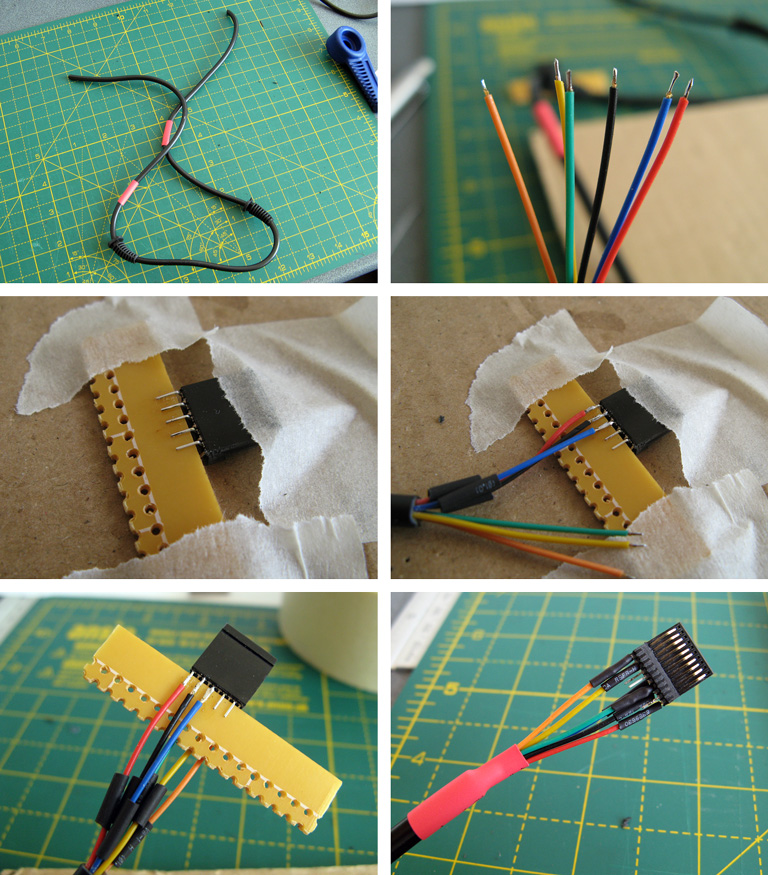
Putting a scrap piece of circuit board material between the two rows of pins also makes soldering much easier. In my case I only soldered the six pins required for this MIDI interface cable:
- 1: +5V
- 3: GND
- 4: RX
- 5: TX
- 8: GND
- 10: +3.3V
Pins are numbered from left to right when looking at the serial port at the rear of the console (if in doubt, you can check the voltages of the end pins against the console's metal chassis ground).
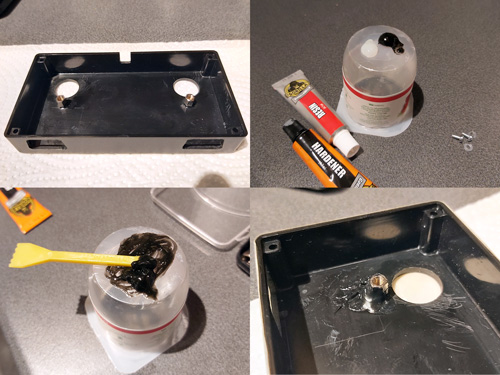
At this point you may wish to double check that your solder connections are made correctly and that nothing is shorted out – try with the cable plugged into the Dreamcast as well, and check that adjacent pins are not shorted together (the only two that should be shorted are pins 3 and 8, the two GNDs). If you're happy with that you can glue the connector onto the backing:
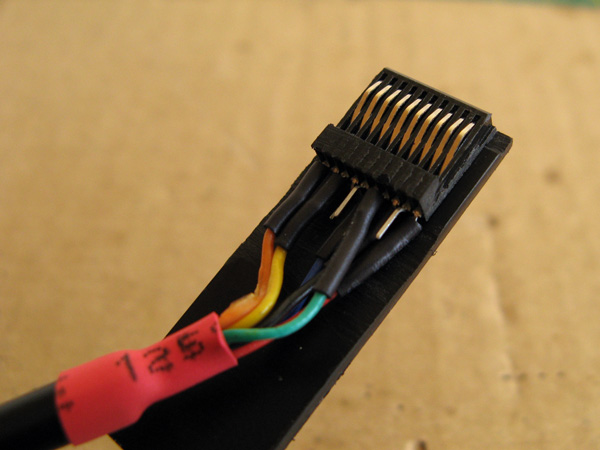

You may notice that this is actually a different connector in the photo to the previous one, and that's because I accidentally got glue into the connector's springy contacts and jammed them so had to start again – definitely not a fun mistake to make, so be careful!
Fortunately, the second one went more successfully. The glued connector snaps in and out of the console with a nice reassuring click thanks to the two holes drilled into the top surface. Before switching on the Dreamcast I tried wiggling the cable around to ensure that even when treated roughly it woudn't short out adjacent pins. When I was happy this was the case I switched on the Dreamcast and ensured that I was getting a consistent +5V from pin 1 and +3.3V from pin 10 – as these pins are at the far end of the connector these are the ones that are more likely to have problems with crooked connectors. In my case I found there was an intermittent fault with pin 1's +5V. This was because I hadn't glued the connector on particularly straight and so pin 1's connector was slightly back from the edge of the backing piece. I very carefully filed the backing piece's edge so that it was flush with the slightly wonky PCI Express connector, after which pin 1 made reliable contact.
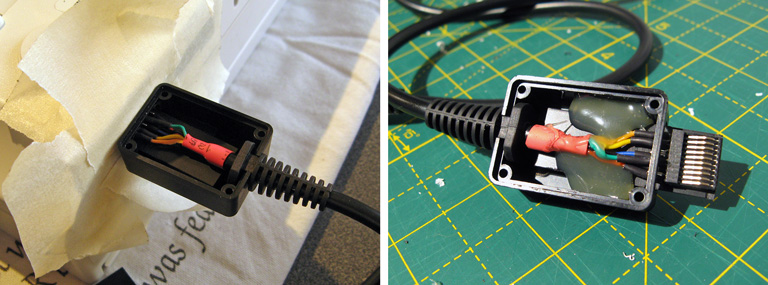
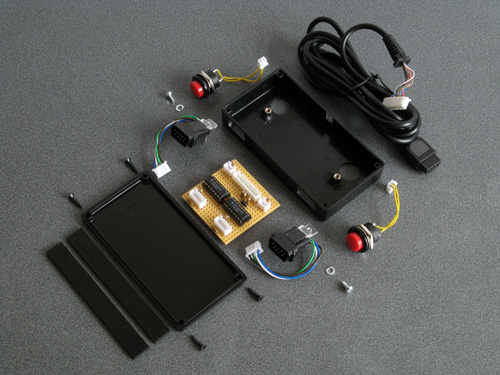
When you're completely happy with the connector, you can make it more robust by putting it inside an enclosure. I have some very small project boxes that are perfect for this sort of thing, it's a bit bulky when compared to the official Sega product but it does its job well here and doesn't bump into the power connector or AV port connector.
I cut a slot in one end of the box for the connector to stick out of and a notch in the other for the cable strain relief to clip into. I surrounded the console's serial port with a few of layers of masking tape to ensure that when the connector was inserted there was still a small gap between the case and the plug to make sure that it could always be fully inserted and not held back by interference from the case (it also protected the console shell from accidental strings of hot glue!) I then plugged the connector into the Dreamcast, made sure that everthing was neatly lined up, and secured the parts in place with copious amounts of hot glue. Once this had set I added more hot glue to the rear of the connector to make sure it was all held as securely as possible, and then screwed the enclosure shut.
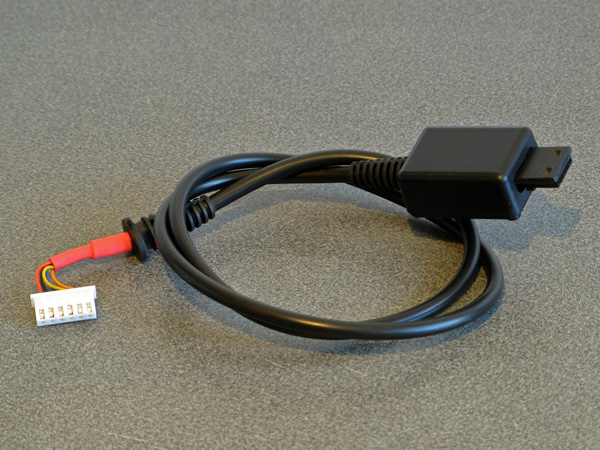

With all the effort spent on the Dreamcast end of the cable, don't forget about the MIDI interface box end! I'm fond of JST-XH connectors so crimped one onto the end of the cable, ready to plug into the circuit board. The finished cable is seen above!
Building a prototype MIDI interface cable
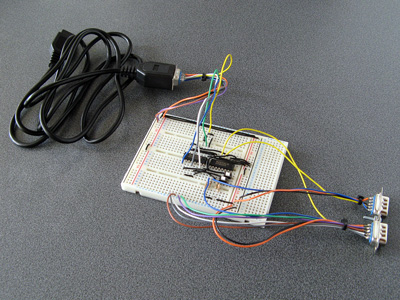
With a Dreamcast serial port cable to hand I was able to experiment and see what happened when using the O・to・i・re (お・と・い・れ) sequencer. Here's the circuit I ended up building on a breadboard:
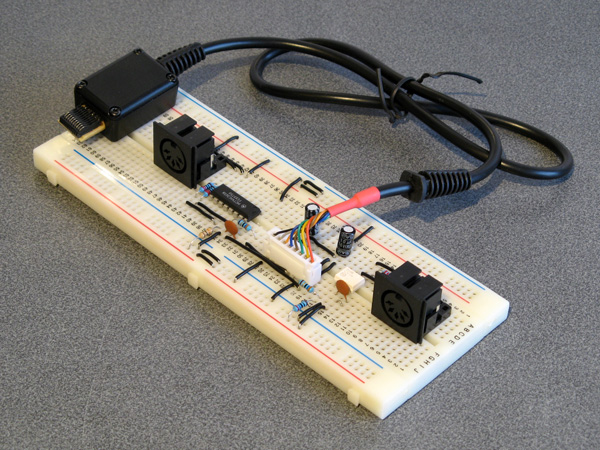
On the very left is the first serial cable connector I tried constructing. It looks more yellow than the final version as I used a piece of pad board for the backing piece instead of the 2mm ABS plastic – I thought I was going to solder the PCI Express connector piece to a circuit board rather than directly to the cable's wires, this turned out to be a mistake. One advantage is that it does have eight wires soldered to it – I thought I'd see what RTS and CTS were doing, but I ended up not using them. The MIDI port to the left is for MIDI OUT and has a large black chip to act as a buffer, the port to the right is for MIDI IN and has a small white chip as an optoisolator. Here's the corresponding circuit diagram:
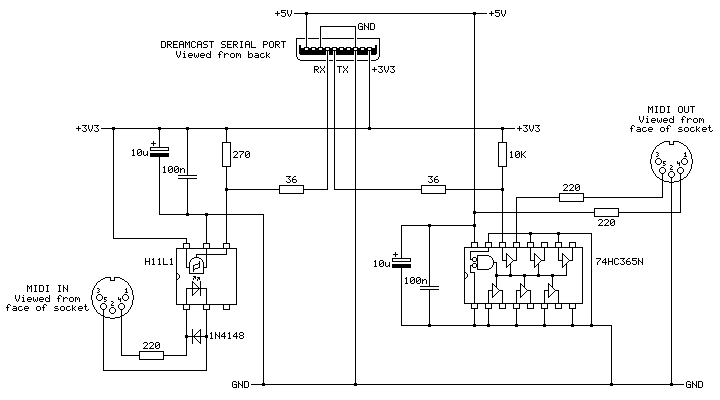
The position of the ports is flipped in this diagram when compared to photo of the breadboard, but it otherwise matches up!
On the left is the MIDI IN port. This uses an H11L1 optoisolator as they are still reasonably easy to get hold of today, are fast enough for use with MIDI and can be run directly from +3.3V. Its output on pin 4 is open collector so it needs the 270Ω pull-up resistor to the +3.3V rail. A +5V-demanding optoisolator could also have been used if it had an open collector output and the pull-up resistor on its output was still tied to +3.3V (we don't want to run +5V into the Dreamcast's +3.3V logic!) but this makes the wiring a little more complicated so sticking to a +3.3V-compatible part makes life easier.
The 36Ω resistor between the output of the MIDI IN circuit and the serial port's RX pin is there because it is in the official cable. The official cable also places ferrite beads on every I/O pin (and has a ferrite bead clipped onto the cable itself) which I have not replicated in my own cable, but they can't hurt and I suppose it could protect the console from certain direct shorts!
The MIDI OUT port uses a 74HC365N to convert from the serial port's +3.3V logic to +5V to drive the MIDI output. MIDI signals can be run from +3.3V (it's the flow of current that's more important than the selected voltage) but +5V seems more typical so I thought I'd stick with that, and as we need to buffer the signal anyway (I'm not sure how much current the Dreamcast's serial ports are designed to sink or source) using the +5V supply we have available to us made sense. The voltage threshold for a "high" input signal is probably a bit too high with the 74HC365N – +3.3V is pretty close to the recommended values in the datasheet, so the 74HCT365N version of the chip would give you more margin for error and would be a drop-in replacement. In my testing the 74HC365N does work well, though, and it's what I had available.
The cable used in this prototype has eight connections rather than the six in the final. This is because I did experiment with the RTS (pin 6) and CTS (pin 7) signals from the console, however as far as I can see these are just pulled low and high respectively and do not change from the moment the console boots, even when sending and receiving MIDI data within the O・to・i・re (お・と・い・れ) software. If they were planned to be used for some purpose then I'm not sure what, and with only one piece of software released to test with I'm not sure I'll find out.
In any case, with this circuit data from the MIDI IN port is translated to +3.3V logic levels suitable for the Dreamcast's serial port input (RX) and translated back from the serial port output (TX) to a current loop suitable to drive a device connected to the MIDI OUT port. In practice it seems this MIDI OUT port acts more like a MIDI THRU with the O・to・i・re (お・と・い・れ) sequencer – any data sent to the MIDI IN port comes straight back out of the MIDI OUT port, however if you record some notes in the sequencer and play them back afterwards they aren't played back out of MIDI OUT. At first I wondered if I'd made a wiring error (accidentally connecting MIDI IN straight to MIDI OUT) but the MIDI OUT is indeed under control of the software as it will stop relaying messages on certain screens.
Putting it all together in a nice box
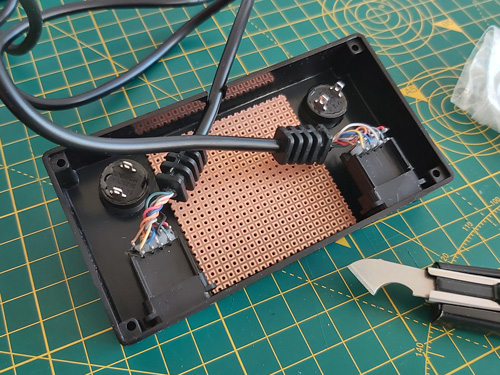
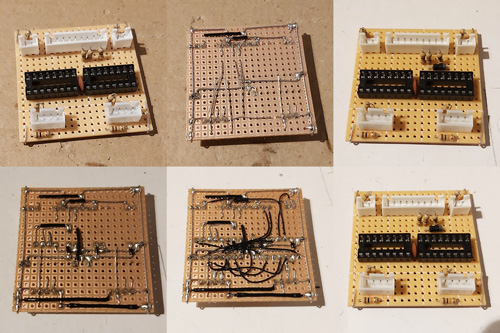
I ended up using my usual pad board construction technique to build the final device:
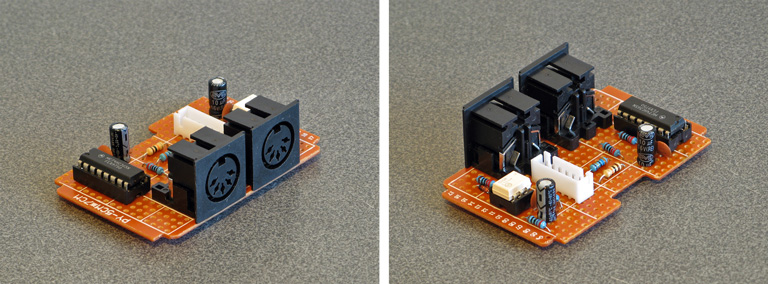
I followed the circuit diagram I'd drawn earlier (rather than copy the breadboard circuit) to ensure the diagram was correct. This was all assembled to fit in a ready-made ABS enclosure, into which I cut some holes. Historically I've had a hard time cutting neat round holes in plastic enclosures – I have a few hole saws and these are great for cutting through wood or acrylic but when trying to cut ABS they tend to bind and either rip the box out of the vice or just shatter it. I normally resort to drilling lots of very small holes around the perimeter of the circle and then try to file it to size, which is OK for buttons or sockets with overhanging parts to hide the inaccuracies but wouldn't do here! For this project I bought a very cheap step drill set on eBay (three bits for a fiver) with zero expectations but it did an excellent job, it kept the centre hole I'd started from and didn't need very much cleaning up. I wish I'd bought one sooner!

The other enclosure challenge to deal with was labelling the two ports. I normally get away without labelling my projects because the function of each port can be guessed quite easily (e.g. inputs and outputs normally only plug in one way, or player 1 is on the left and player 2 is on the right) but in this case there's not much convention for where MIDI OUT and MIDI IN go (though the original Dreamcast MIDI interface cable puts MIDI OUT on the left, as does my M-Audio Midisport). For this I thought I'd try using some dry transfer lettering designed for model-making, and it seems to do a great job!

I'm pretty happy with the final outcome – it's a bit of a pain making the serial cable for connection to the Dreamcast, but the end result works well and it saves spending an absolute fortune on the original Sega accessory.
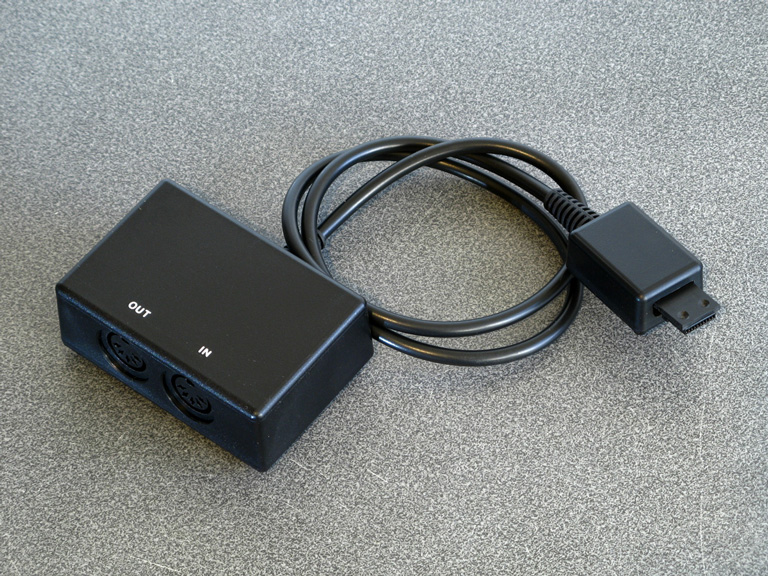

Now I can get on with making music with my Dreamcast!
Connecting an old receiver/amplifier to an HDMI television, apropos achieving surround sound
Sunday, 16th August 2020
Now that the charity shops have reopened in the UK I enjoy hunting for good bargains and recently picked up a DAV-S400, a home cinema system originally sold back in 2002. I was not particularly interested in its DVD playback capabilities, especially as it only outputs composite video, but the integrated 5.1 surround sound amplifier and optical input made me think that I could use it to replace my current stereo amplifier for a better home cinema experience. The inclusion of SACD support was an added bonus as I'd bought myself a copy of The Dark Side of the Moon in that format back in 2004 and only been able to listen to it once, so if I couldn't get the home cinema side working at least the SACD part was self-contained and I'd be able to enjoy that.
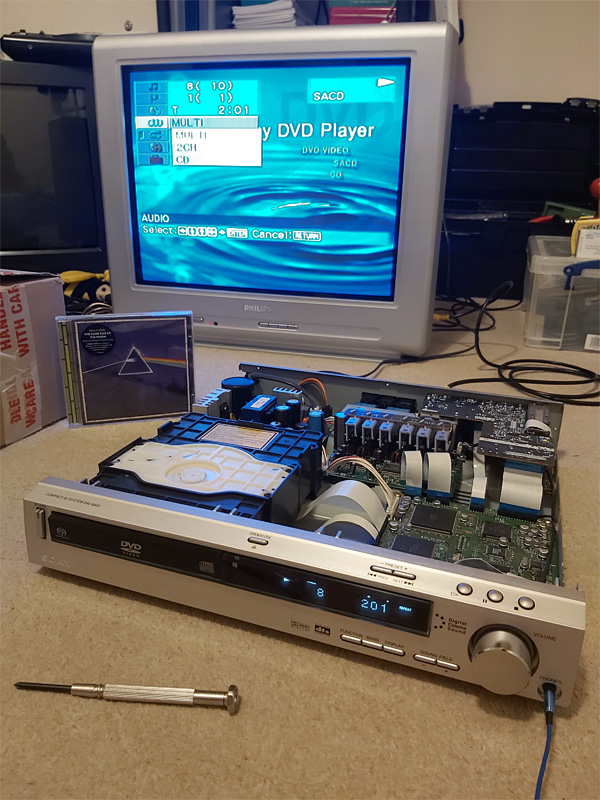

This ended up being quite the learning project for me and I had to solve quite a few problems along the way. I'm still not entirely sure if I've found the best solutions in places but I thought I'd write this post in case it helps anyone else hooking up an old receiver/amplifier to a modern HDMI system!
The proposed setup
I watch most media using my Windows PC as a source. The PC is in one room and the TV is in another and long HDMI and USB cables run between both under the floorboards. An HDMI splitter is also used near the PC so it can drive its main monitor and the TV in the other room simultaneously.
I was previously running analogue stereo audio from the headphone socket of the TV to a stereo amplifier with a line level "super woofer" output that ran to a separate amplified subwoofer for 2.1 sound.
I knew that HDMI could carry digital audio, and both my monitor and TV have digital outputs. As the DAV-S400 has a digital input, I could just connect that to the digital output from the TV (instead of the headphone output) and in my naivety assumed that's all it would take to have glorious multichannel digital audio. Of course, things are rarely that easy…
My TV only has coaxial digital audio out via an RCA connector and the receiver has an optical input via a TOSLINK socket. Fortunately, my PC monitor has an optical output so I connected that to the receiver for the sake of testing. When I played media on my PC sound came out of the speakers, however only in stereo, even from 5.1 sources. What was going on?
Capabilities of S/PDIF
The digital output from the monitor/TV and the digital input of the amplifier operate with S/PDIF digital audio. This can carry two channels of uncompressed PCM audio for regular stereo. To carry 5.1 multichannel audio the data needs to be compressed using Dolby Digital or DTS. The DAV-S400 supports both, but you need to find a way to transfer that compressed signal to the receiver first.
Foiled by the EDID
Here is the biggest fly in the ointment! Extended Display Identification Data (EDID) is metadata that an HDMI display provides to describe what sort of video resolutions and sound formats it supports. All three of my HDMI devices (the HDMI splitter and both displays) report that they support two-channel PCM audio but nothing else.
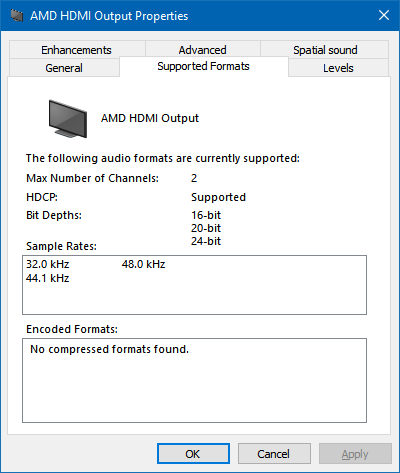
As a result, devices will only try to send stereo PCM audio to them and not Dolby Digital or DTS. If you have a sound card with an S/PDIF output you will notice that you can go in to its "Supported Formats" tab in Windows and tick which features the receiver supports – this is as the receiver can't tell the sound device which formats it supports automatically like an HDMI device can via its EDID. Unfortunately, Windows trusts the EDID and doesn't let you go in and enable support for features the display doesn't claim to provide. An easy solution here would be to just use my sound card's S/PDIF output but I didn't fancy taking the floorboards up again to run another cable…
A custom monitor driver to override the EDID
Fortunately you can create a custom monitor driver with a "fixed" EDID that advertises support for Dolby Digital and AC3 using a couple of easy tools.
The first piece of software you'll need to use is EnTech's Monitor Asset Manager – this will allow you to extract the current EDID to a file and will later let us turn the updated EDID back into an installable driver.
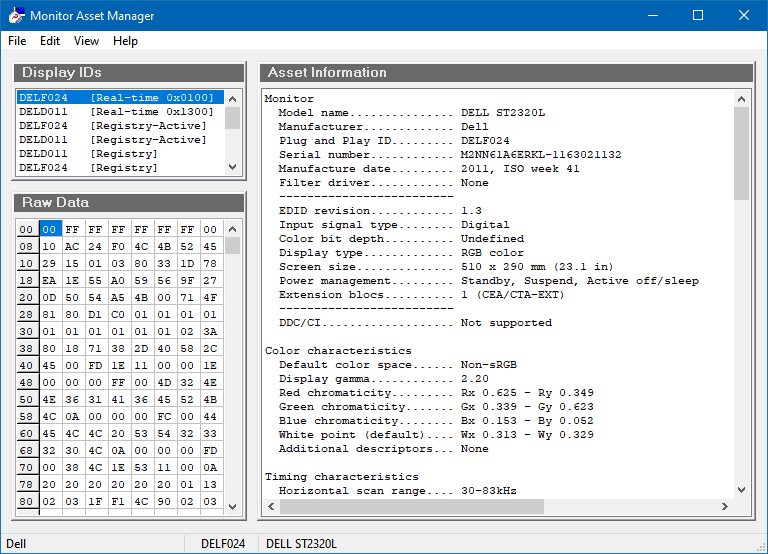
Run the software and find the monitor that is connected to the HDMI port that you are going to be outputting sound to from the list in the top left. In my case that's my HDMI splitter (which for some reason identifies itself as a DELL ST2320L). Save the EDID to a .bin file via the File→Save as menu item.
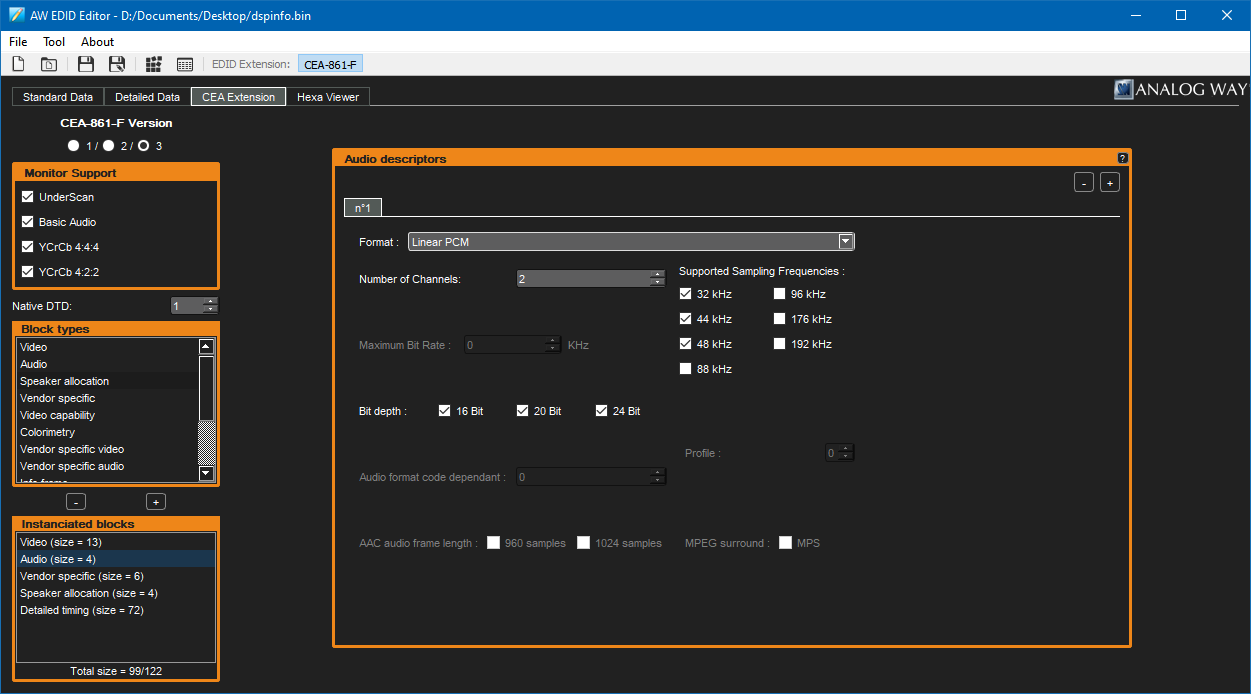
Now that you have your EDID data exported to a file, you'll need to edit it. A nice idiot-proof way to do so is with Analog Way's AW EDID Editor. Run the software and open the .bin file for the EDID file you just saved. Switch to the CEA Extension tab and you will probably see that it only reports support for stereo uncompressed PCM when you look at the "Audio" block.
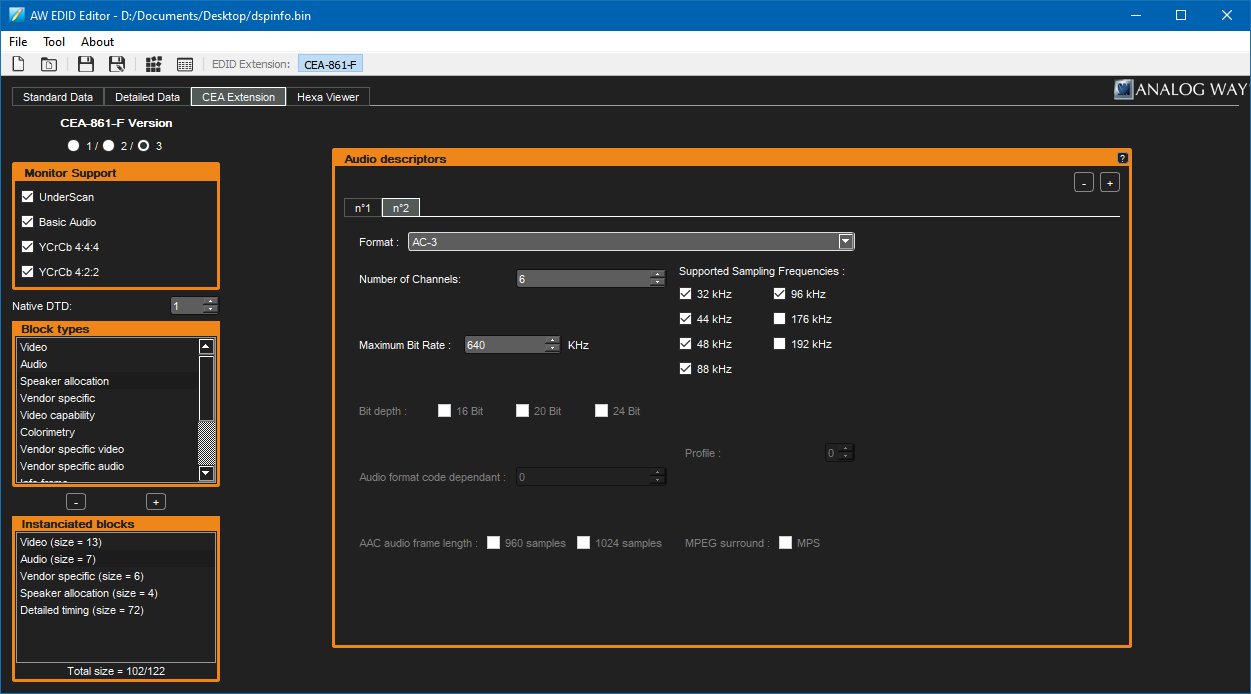
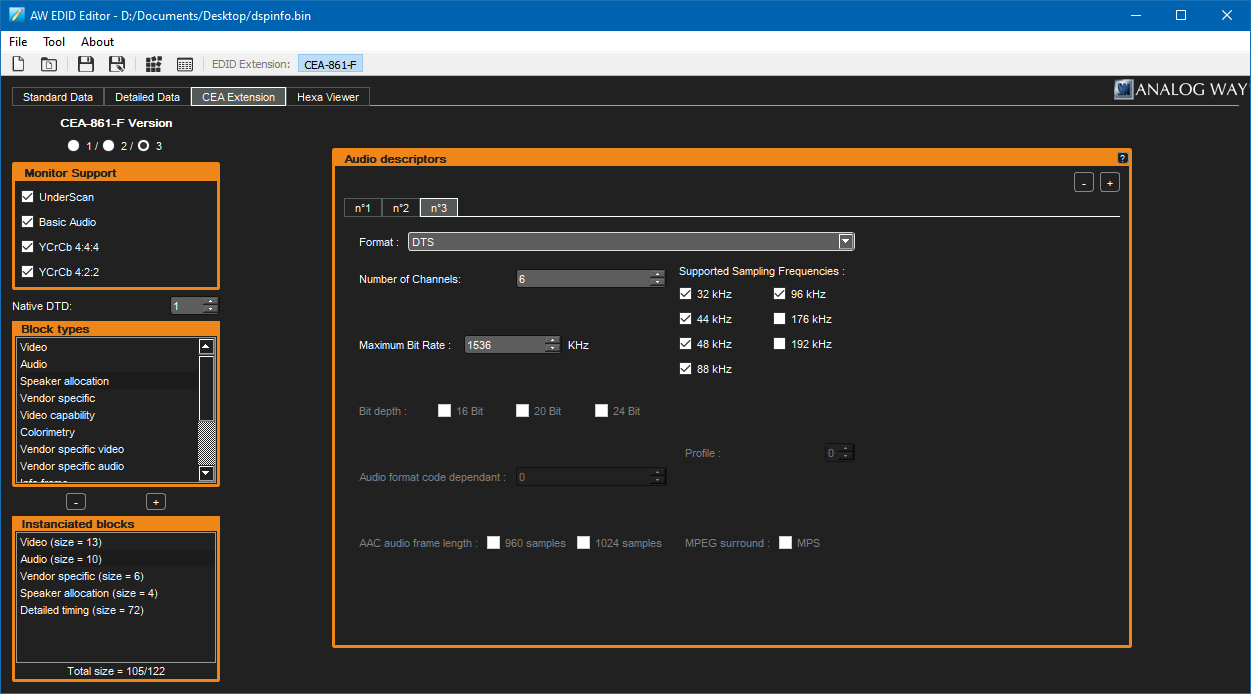
At this point, you can add audio descriptors according to the capabilities of your receiver. I'm not entirely sure what the best values to enter here are, especially when it comes to bitrate – as far as I'm aware DVDs usually use up to 448kbps for Dolby Digital AC-3 and up to 768kpbs for DTS but there's a more concrete limit of 640kbps for AC-3 and 1536kbps for DTS so these are the values I've used when setting up my EDID.
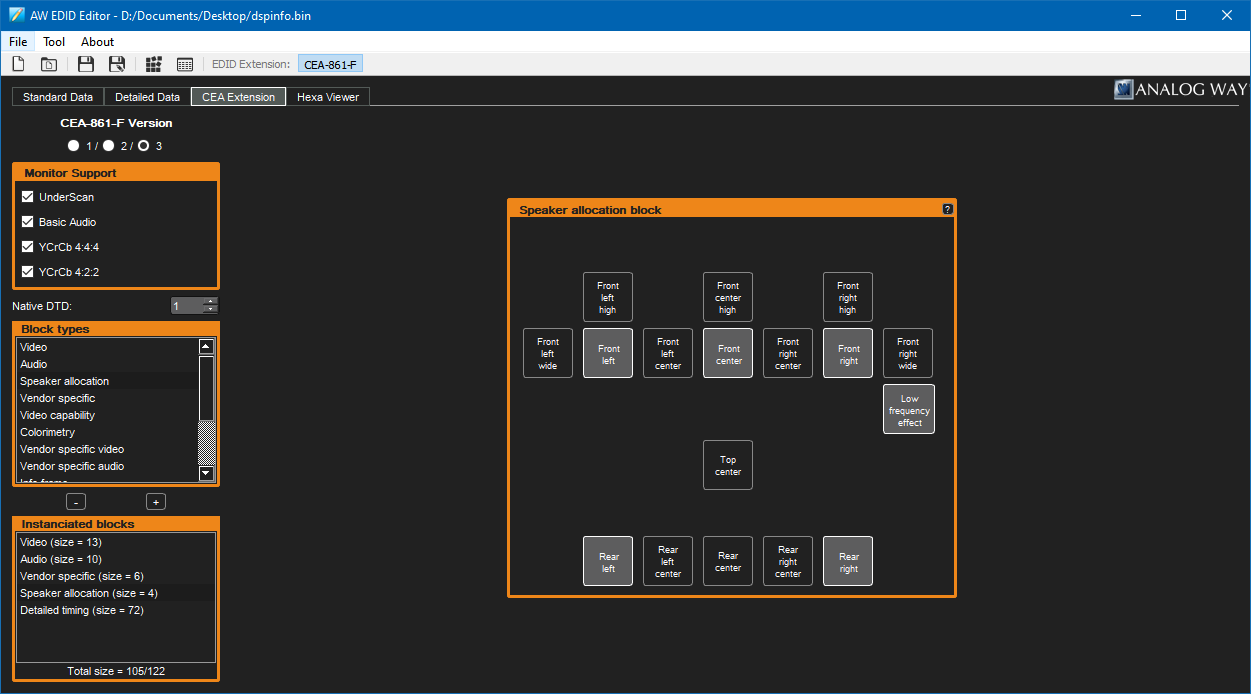
You can also use the "Speaker allocation" block to specify which speakers your device has attached – in my case I've set this up to match my 5.1 setup. Save the EDID at this point, and you're ready to create the custom monitor driver!
Go back to EnTech's Monitor Asset Manager and open the saved .bin file for your new EDID. Click File→Create INF and save the INF to create your new monitor driver. Easy!
What's less easy now is installing that driver on a modern 64-bit version of Windows, as the driver is unsigned and Windows will not let you install unsigned drivers normally. To save headaches at this point I'd recommend looking up how to enable the installation of unsigned drivers, but at the time of writing this is how it's done in Windows 10 (this will involve restarting your computer):
- Click Start→Power
- Hold Shift, then click "Restart".
- At the "Choose an option" screen, select "Troubleshoot".
- At the "Troubleshoot" screen, select "Advanced options".
- At the "Advanced options" screen, select "Start-up Settings".
- At the "Start-up Settings" screen, click "Restart".
- Once the computer has restarted, select the "Disable driver signature enforcement" option (F7).
When the computer has restarted, you should be able to install your unsigned monitor driver. To do this, go into Device Manager and find the entry for your HDMI device in the "Monitors" section.
- Right-click your device and select "Update driver".
- Select "Browse my computer for drivers".
- Click "Let me pick from a list of available drivers on my computer".
- Click the "Have Disk..." button.
- Browse for the monitor.inf file you created previously, then click OK.
- Select the EDID Override option that appears in the list and click "Next".
- Click "Install this driver software anyway" when prompted by the unsigned driver warning dialog box.
At this point, you will likely need to restart again but all being well after doing so you should now see that Dolby Digital and DTS Audio are now listed as supported encoded formats in the Sound control panel.
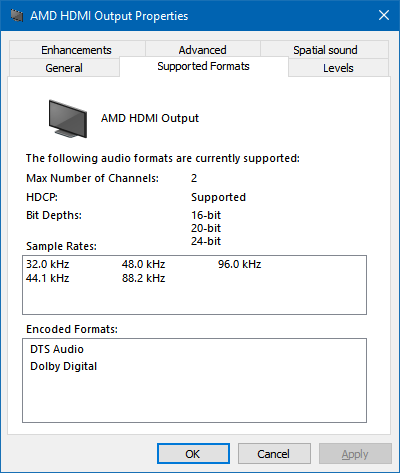
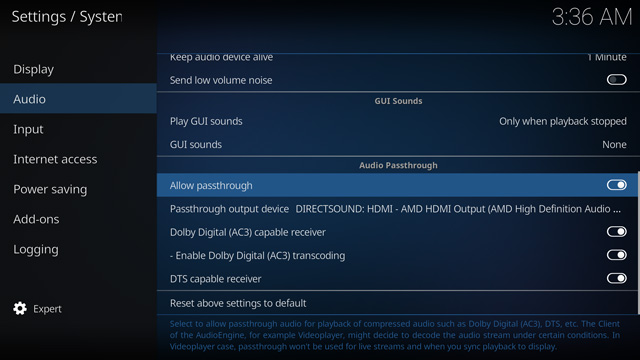
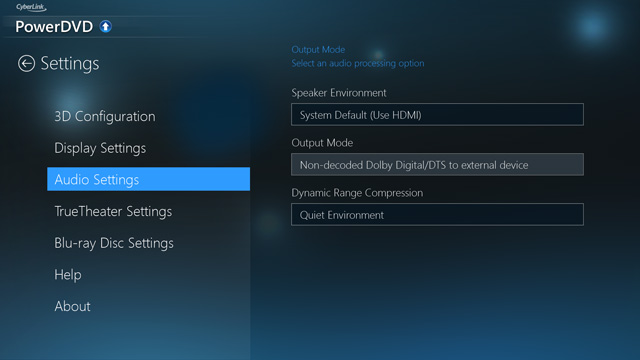
Passing through Dolby Digital and DTS without conversion to PCM
Getting Windows to believe that your receiver supports Dolby Digital and DTS over HDMI is the trickiest problem, but you still need to ensure that the compressed audio gets through every step of the way from the media to the receiver.
You will need to ensure that your media playback software is configured to pass through the audio directly rather than decoding it to PCM. If your software has an audio settings menu option, ensure that that is set to allow non-decoded audio to pass through.
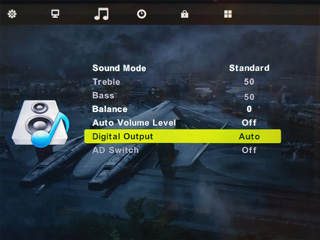
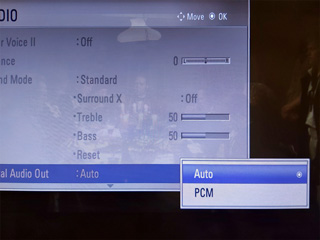
You will also need to ensure that your display is configured to pass through the audio without decoding it to PCM – check its sound menus for the relevant options, and change any settings to "Auto" or the appropriate equivalent instead of "PCM".
In my case I was testing with the receiver connected to my PC monitor via its optical output. Dolby Digital worked fine, however DTS was not working at all. I found that if I enabled the monitor's internal speaker it would output sound when fed Dolby Digital but not when fed DTS, however my TV would output sound when fed either. It seems that my PC monitor genuinely lacks support for DTS and won't even pass it out of the digital output port – fortunately when I acquired a coax to optical adaptor for my TV I found that it passed through DTS just fine!


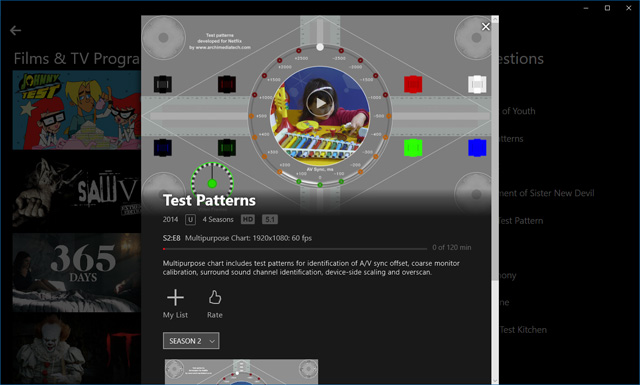
The Windows 10 application version of Netflix also supports 5.1 audio over Dolby Digital and didn't need any further configuration. If you search the library for "Test" there's a useful selection of test patterns that can be used to ensure your speakers are set up correctly.
Other notes
I have a separate Blu-ray player attached to my TV as my PC's video card displays corrupt video when decoding Blu-ray 3D unless I install very old versions of its drivers and I thought a separate Blu-ray player was an easier option than dual-booting into Windows Vista. Unfortunately, my Blu-ray player believes my TV's EDID and refuses to pass-through Dolby Digital or DTS over HDMI even when set to output "bitstream" audio. Fortunately it has a separate coaxial digital audio out that outputs Dolby Digital or DTS even when it's outputting PCM over HDMI but it does mean I need to add a switch box for the single digital input into the receiver which is slightly less elegant than running everything through the TV. There are standalone EDID spoofers that plug in between your device and the monitor that may be able to resolve this issue in the same way the custom PC driver did but these are not inexpensive so I have not been able to test this myself.
The DAV-S400 is extremely fussy about reading hybrid SACDs, and will often detect them as regular CDs. Ejecting and closing the tray persuades the machine to re-scan the disc, so if you have problems press the "DVD Display" button to ensure the OSD is visible and double-tap the eject button to quickly eject and close the tray until the indicator in the top right of the screen reads "SACD" instead of "CD".
If it does detect it as an SACD it will then play it absolutely flawlessly, the issue only seems to be with the initial format identification. I was able to improve the success rate with Dark Side of the Moon by carefully cleaning the drive lens, however I couldn't get Brothers in Arms to be detected at all until I went into the service menu and recalibrated the drive. You can do this by switching the machine on in DVD mode, holding the Stop+Display buttons on the unit together and rotating the volume wheel clockwise. From here go into "Drive Auto Adjustment". I initially tried calibrating with an SACD (labelled "LCD" in the menu) but this didn't help, so I tried the "All" menu option which prompts you to insert a single-layer DVD (DVD-SL), CD, then dual-layer DVD (DVD-DL). After this point it doesn't automatically prompt for an SACD so I left this in the default settings rather than calibrating and to my surprise found that Brothers in Arms now works (and, once detected, plays flawlessly). This inability to handle hybrid SACDs correctly seems to be a common flaw with Sony players of this vintage, unfortunately.
On a more practical note, I needed to find a way to attach my speakers to the amplifier, which had connectors that exposed a pair of pins around 6mm apart. Following a hunch I bought some Tamiya power connectors and found these to be a good fit once you cut off the retaining clip!
I did however find that a couple of the audio channels were intermittent and when I took the case lid off was surprised to see that one of the electrolytic capacitors on the amplifier board was barely held in by any solder at all and when I touched it it let out a big fat noisy spark! I resoldered it in along with all of the audio transformers, connectors and relays on the amplifier PCB which fortunately restored all audio channels back to their former glory.
All in all this has been quite a learning experience, though having now watched Terminator 2 and Mad Max: Fury Road with 5.1 surround sound I can definitely say it was worth it.
The completed Light Phaser to Justifier adaptor
Wednesday, 29th April 2020
Since my previous post I've had a chance to test the Sega Light Phaser to Konami Justifier adaptor circuit with Lethal Enforcers II: Gun Fighters and it seems to work well throughout the game so I thought it was a good time to put the project into a neat box.
The Mega Drive uses common DE-9 connectors for its controller ports. You can easily find metal connectors with lugs for panel mounting however I wanted to use plastic connectors similar to the ones on the original console – not just for a consistent look, but to also protect the plastic connectors on the Sega Light Phasers from being scratched by the sharp edges of metal connectors. I'm using controller extension cables for the nice moulded connector and cable that plugs into the console, so thought I'd look at the controller socket end. Squeezing the bottom half of the connector splits the two halves apart and you can use a spudger or similar tool to pop the casing open and retrieve the connector – just what I needed!
I nearly always put my projects in off-the-shelf enclosures, cutting and drilling holes in them where required. In this project's case the most awkward holes to cut will be for the controller connectors as they do not have an external lip to mask any poorly-cut holes. As such, I thought I'd start here:
My process here is a bit tedious, but gets the job done – I cover the enclosure in masking tape, then mark out where the holes should appear. I use a drill to make several holes inside the shape I wish to cut out, then use a router bit or sharp knife to cut between the holes to open up the hole properly. A set of hand files is then used to bring the hole to its final shape and size, checking against the connector along the way to ensure an accurate fit.
The circular holes for the buttons are cut in a similar fashion, except that as the buttons have outer lips that cover the borders of the hole the outer edges don't need to be quite as precise and a larger router bit and drum sander can speed up the job considerably rather than having to rely on careful hand filing.
A rectangular notch was cut in the rear centre of the case for the cable to the console to exit through and the parts were then loosely installed for a test fit. A piece of pad board was cut to size by scoring it and snapping it over the edge of a table. I wanted it to be as large as possible to make it easier to fit all of the components and wires in, but could the case be closed with the cables and connectors in place too? To make sure it would I thought I'd start with the bulkiest of cables, the one that goes to the console.
I attached a nine-pin crimp connector to the end of the controller cable to plug into the pad board and experimented with the placement of the destination connector – I found that four rows down was about the closest it could go to the top edge of the board whilst still providing enough room for the cable coming in to bend neatly out of the way.

The various parts for the console output connector, light gun input connectors, start button connectors and multiplexer chip DIL sockets were placed on the pad board without soldering to get a rough idea of the final layout and component spacing, ensuring there was enough space around each part to install other components or wires. Once a rough idea was in mind, the main soldering work could begin!
Not much appears to happen between the first and final stages, as most of the work takes place in the wiring on the bottom of the board. Connections that can be made in straight lines without crossing other connections are soldered first, followed by straight connections that cross other connections that can be insulated by slipping on a piece of insulation stripped from a reel of wire. When all of the easy connections are made in this way the outstanding connections are made by soldering lengths of thin wire wrap wire between points on the underside of the board. As each connection is made it is crossed off the circuit diagram – this allows me to check that the circuit diagram is correct, as if I can replicate the circuit from this diagram it's a pretty good indication that it's safe for other people to use to make their own versions of this project.
The DE-9 sockets used for the Light Phaser inputs have all nine pins soldered to the cable by default. We only care about four of them (VCC, GND, TL and TH) and as we don't have enough room for all nine connections to be soldered to the board four-pin connectors are used instead. The old wires are unsoldered and new wires and crimp connectors are attached in their place. This let me check that the circuit board was otherwise working fine, but I still need to figure out how to mount these connectors securely inside the enclosure. I was initially thinking of just holding them in place with hot glue, but this is not very elegant and makes future maintenance much harder! The DE-9 sockets do have a flat surface at the top that is only slightly more than 5mm from the top surface of the enclosure, and I do have some 5mm PCB standoffs that could be handy…
I cut a 9mm wide strip of acrylic from 2mm thick sheet which fits neatly into the top channel of the DE-9 connectors. I then cut it into short sections that could be glued together into Z-shaped brackets. The long section of the "Z" mounts to the DE-9 connector and the short section has a hole drilled through it so it can be secured to the PCB stand-off with a screw. The arrangement is then test fit inside the enclosure using double-sided sticky tape to check that a solid mount is possible – the screw to the PCB stand-off accounts for one part of that mount, and the tight fit of the connector inside the D-shaped hole in the enslosure accounts for the other part.
When it seems like a good fit is possible the Z-shaped brackets are glued to their DE-9 connectors. The DE-9 connectors are then installed in the enclosure with some glue on the bottom of the PCB stand-offs – when everything is lined up neatly this glue secures the stand-offs in the right position, albeit not very strongly.
Once the glue had set the screws were removed and the DE-9 sockets were carefully removed. Two-part epoxy was then applied liberally around the PCB stand-offs to provide a bit of extra support. Unfortunately, the stand-offs are very close to the nuts used to secure the start buttons to the enclosure and as such not much epoxy could be placed on that side but hopefully the rest should provide enough support.
Whilst the epoxy was curing the final parts of the project could be assembled – a pair of start buttons had wires soldered to them with crimp connectors on the other end and a couple of rubber strips were cut to provide a bit of extra grip to the bottom of the adaptor. The various component parts of the project can be seen in the photo above.
Everything does fit fairly neatly inside the enclosure, fortunately! After everything is assembled inside the bottom of the enclosure was screwed on and the rubber grip strips attached with double-sided sticky tape.

I still haven't been able to test this adaptor with any Mega CD games however it does work well in both Lethal Enforcers and Lethal Enforcers II: Gun Fighters on the stock Mega Drive so hopefully it will also work well in Mega CD games.
I'm pretty happy with how this project turned out. If you would like to assemble the adaptor yourself, you can find the schematic in the previous journal entry, and if you do build it I'd love to hear how you got on!
Adding some protective resistors to the Light Phaser to Mega Drive gun adaptors
Monday, 20th April 2020
Here's a quick update to the two Mega Drive light gun adaptor circuits, all to a few extra resistors in and around the adaptor and the console.
The real Sega Menacer receiver drives the TH line (used to indicate when the gun has seen light) directly from the output of a NOR gate with a 470Ω resistor in series. My circuit uses a transistor in the open-collector configuration with a 10KΩ resistor on the base input and a 1KΩ pull-up resistor, which is the same as the circuit used in the original Sega Light Phaser.
In a worst-case scenario the console could configure TH as an output, drive it high, and the Menacer adaptor could drive TH low at the same time. This would short the console's TH output to ground via the transistor, and might damage it (I'm not sure how these I/O ports are constructed internally). The TH output from a regular Sega Light Phaser would have the same problem, however that only pulses low briefly when it sees the light from the CRT whereas the TH output from the Menacer adaptor is latched and can stay low for a much longer time, increasing the risk. Resistors are cheap, so assuming the engineers at Sega know their hardware better than I do I thought it safer to add a 470Ω resistor on the TH output. This hasn't affected performance, as far as I can see. I also corrected the diagram to reference the BC548 as this is the transistor I tested with – the BC547 probably works too, however in the interest of accuracy I thought it best to stick with what I know works.
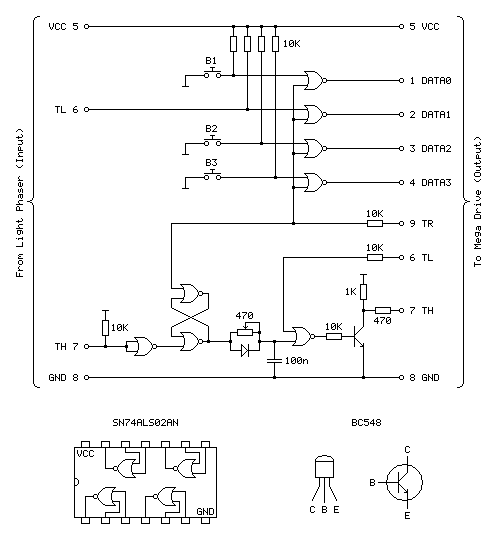
Sega Light Phaser to Sega Menacer adaptor
The Menacer circuit (as well as the original control pad) drives the DATA0~DATA3 lines directly so I haven't included any resistors there. I have, however, applied the same resistor changes to the Justifier adaptor:
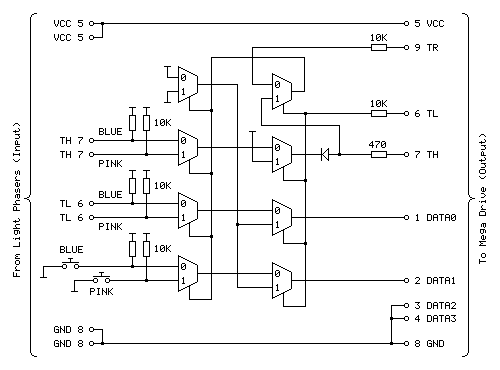
Sega Light Phaser to Konami Justifier adaptor
As well as the 470Ω resistor on the TH input/output line I have added the 10KΩ resistors on the TL and TR input lines. I'm still not sure what these are for but as they are there in the Menacer adaptor and as Sega presumably know best I've included them here for completeness. As these are attached to inputs on the logic gates there should be very high impedance anyway, but it could be for protection in case the logic gates are improperly powered. What I do know is that the extra 10KΩ pull-ups on the TH inputs from the Light Phasers should protect against spurious TH outputs when either of the guns are unplugged.
I still haven't been able to test the circuit with any other games, but for now these two circuits seem to be holding up!
Simplifying the Light Phaser to Justifier adaptor to a two-chip solution
Saturday, 18th April 2020
In the previous post I mentioned I was dissatisfied with the optimisation of the Light Phaser to Justifier adaptor circuit. This was because I was using two quad two-input multiplexer chips (eight multiplexers total) but only using three multiplexers on each chip but also needed two inverter gates and so had to add a third chip to accommodate that requirement. It seemed like there must be a better solution, and after pondering this in the shower I think I found it.
One of the inverters is required for the transistor used to drive the TH line from the circuit. The TH line is bidirectional, and from our end of the circuit is either left floating (where it can rise high) or pulled directly to ground. To achieve this I was using an NPN transistor with the collector connected to TH, the emitter connected to ground and the base connected (via a resistor) to our logic signal. Unfortunately, such a transistor is switched on by a positive voltage and so a logic high at the input resulted in a logic low on TH, so to correct this an inverter was added.
A much simpler solution is to get rid of the inverter and transistor entirely and to replace it with a reverse-biased diode, replacing three components with one:
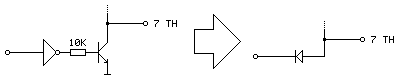
Current can only flow the diode if the voltage at the anode (right, connected to TH) is higher than the voltage at the cathode (left, connected to our logic signal). This means that if our logic signal is the same as the current state as TH then no current flows (and so we leave TH alone) and if our logic signal is high and TH is low then the diode is "backwards" and no current flows. The only way we can influence TH is if it is high and our logic signal is low, allowing current to flow through the diode, grounding TH – which is our desired outcome. One inverter is out of the way!
The other inverter is used to produce an inverted version of TH which is used when the console is retrieving the peripheral ID from the Justifier. We can use a multiplexer as an inverter by using the select pin as the input, tying the "0" input high and the "1" input low (that way when 0 is requested 1 is output and when 1 is requested 0 is output). The problem we have here is that all four multiplexers on a chip share a common selection pin, we need to invert TH, and neither of our two multiplexers is using TH as the select pin (one is using TR to select between the two guns and the other is using TL to globally enable or disable the guns).
The solution here is that we only need this inverted TH signal during the peripheral ID check which is carried out when the guns are globally disabled. When the guns are disabled we don't care about what the TR gun-selection multiplexer is doing, as whether the blue gun or pink gun is selected is irrelevant as the data never makes it to the console. We can therefore use the spare multiplexer on the TL-selected multiplexer chip to select between TR and TH, and use the output of this as the select pin into the multiplexer chip previously used to select between the two guns and use its spare multiplexer as the inverter.
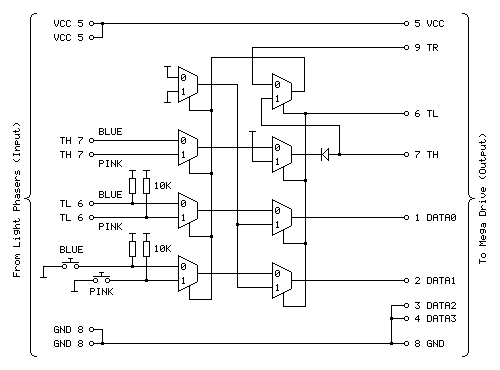
The revised circuit is shown above, the wiring is more complicated than the previous one however it takes advantage of all eight multiplexers on both chips and does away with the need to have an additional inverter logic chip and transistor driver circuit for TH.
The revised two-chip prototype is picture above, and has been tested successfully with Lethal Enforcers – performance doesn't seem to be any different from before, which seems to be a good sign!